| Development of new suistainable methods in organic synthesis |
Organic Synthesis is, of course, the very core of the research group ISYMECH. Without efficient synthetic methods to obtain our molecules of interest, like non-natural aminoacids, peptides, oligomers, natural and bioactive compounds, further applications would not be possible. Particular attention is paid to the development of green methods, thanks to the use of catalytic reactions or supported catalysis. Global issues like climate change, water shortages and natural resource scarcity, challenge particularly chemistry to find high yielding methods with a lower environmental impact, to develop a suistainable world.
| Synthesis of bioactive compounds for biomedical applications |

Medicinal chemistryis is a broad and multidisciplinary topic which requires different expertises like chemistry, physics, biology and pharmacology. We aim to support the global efforts for health, preventing, treating, or curing diseases through the design, synthesis and screening of new new chemical compounds.Specifically, we are interested in:
- The development of new antimicrobial molecules or materials to fight the insurgence of antimicrobial resistance.
- The design and synthesis of new antitumoral compouds
- Synthesis of neuropeptide mimetics for neurological disorders, especially Alzheimer and Rett Syndrome
- Development of materials for surgical and aesthetic medicine
| Synthesis and Conformational Studies of Secondary Structures |
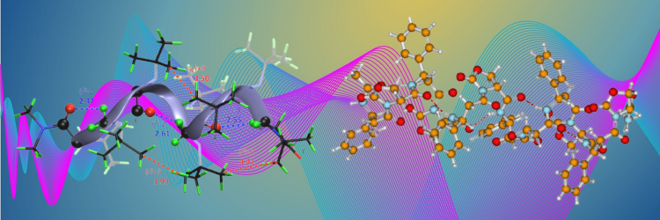
Conformational diversity is the way of Nature to disclose fundamental properties. We are interested in the mimic of natural oligomers and biopolymers. A deeper knowledge on the conformational and structural geometries at a molecular level allows a fine tuning of macroscopic properties. The use of a bottom-up approach leads to the synthesis of new compounds and materials for many different apllications, following the path from structure to function.
- Synthesis of new foldamers, oligomers able to fold in stable conformational structure thanks to specific attractive or repulsive interactions between sites remote in sequences, like solvophobic effects, hydrogen bonding, local conformational restrictions, internal constrain or other stabilizing interactions. The comprehension of these properties and the possibility to design and synthesise specific sequences are of great importance in medicinal chemistry, especially to target protein-protein interaction domains, an approach of increasing interest in science.
- Synthesis of amphiphilic molecules based on peptidomimetics for the selective formation of self-assembly materials, like micelles, vesicles, nanotubes or artifical membranes.
- Synthesis of new chiral metal chelators based on natural peptides and derivatives for chelation therapy


